Abstract
Review Article
The coral crunch: Amyloidoma
Anubha Bajaj*
Published: 20 January, 2021 | Volume 5 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-005
Amyloidoma is an exceptional, progressive disorder demonstrating a characteristic accumulation of significant quantities of amyloid within soft tissues. Amyloidoma is additionally nomenclated as tumoural amyloidosis, nodular amyloid or localized amyloidosis. Furthermore, insulin-derived amyloidoma is referred to as insulin ball. Amyloid is a protein polymer configured of identical monomeric protein units wherein pathological variety is articulated from misfolded proteins. In excess > of twenty three subtypes of proteins can configure amyloid fibres in vivo. Extra-cellular or intra-cellular deposition of amyloid can modify normal organ function [1].
Amyloidosis is categorized into systemic and localized subtypes. Localized amyloidosis displays a localized mass effect and demonstrates a superior prognosis. Insulin-derived amyloidosis was initially documented by Storkel, et al. in 1983 who recognized accumulated insulin- amyloid fibrils in diabetic individuals subjected to continuous infusion of porcine insulin over a period of 5 weeks or more [1,2]. Amyloid nodules may be associated with systemic amyloidosis.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.adr.1001013 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Antisecretory function; Cross-reactivity; Delayed reaction; Famotidine; Hypersensitivity; Maculopapular exanthema; Patch test; Ranitidine
References
- Musat G, Evsei A, Calina D, Docea AO, Doukas SG, et al. Rare amyloidoma of the tongue base – a case report and review of the literature. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020; 12: 258-262. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32064103/
- Storkel S, Schneider HM, Müntefering H, Kashiwagi S. Iatrogenic, insulin-dependent, local amyloidosis. Lab Invest. 1983; 48; 108-111. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6337294/
- Gertz MA. Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: 2020 update on diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. Am J Hematol. 2020; 95: 848-860. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32267020/
- Samlaska C, Reber S. Murry T. Insulin-derived amyloidosis – the insulin ball, amyloidoma. JAAD Case Rep. 2020; 6; 351-353. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32258319/
- Geller HI, Singh A, Mirto TM, Padera R, Mitchell R, et al. Prevalence of monoclonal gammopathy in wild-type transthyretin amyloidosis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2017; 92: 1800-1805. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29202938/
- Asiri MMH, Engelsman S, Eijkelkamp N, Höppener JWM. Amyloid Proteins and Peripheral Neuropathy. Cells. 2020; 9: 1553. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32604774/
- Westermark P. Localized AL amyloidosis- a suicidal neoplasm? Ups J Med Sci. 2012; 117: 244-250. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22335280/
- O’Reilly A, D’Souza A, Lust J, Price D. Localized tongue amyloidosis – a single institutional case series. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013: 149: 240-244. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23715681/
- Hazenberg BP. Amyloidosis-a clinical review. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2013; 39: 323-345. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23597967/
- Balwani MR, Kute VB, Shah PR, Wakhare P, Trivedi HL. Secondary renal amyloidosis in a patient of pulmonary tuberculosis and common variable deficiency. J Nephropharmacol. 2015; 4: 69-71. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28197481/
- Charlot M, Seldin DC, O'hara C, Skinner M, Sanchorawala V. Localized amyloidosis of the breast – a case series. Amyloid. 2011: 18; 72-75. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21501022/
- Kubota K, Ito R, Furudate K, Kon T, Nakagawa H, et al. Localized AL amyloidosis of the tongue-a case report and literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol. 2017; 29: 142-145
Figures:
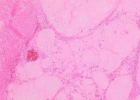
Figure 1
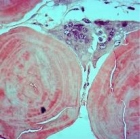
Figure 2
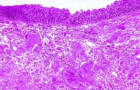
Figure 3
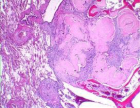
Figure 4
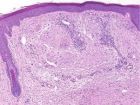
Figure 5
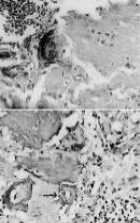
Figure 6
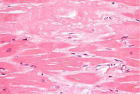
Figure 7
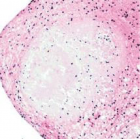
Figure 8
Similar Articles
-
Maculopapular delayed exanthema due to ranitidinePilar Hernández Alfonso*,Idoia González Mahave,Irene Vidal Oribe,Mª Dolores del Pozo Gil,Mónica Venturini Díaz,Teófilo Lobera Labairu. Maculopapular delayed exanthema due to ranitidine. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.adr.1001012; 4: 014-016
Recently Viewed
-
The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution StudyMansouri Nada1, Yaiche Rahma*, Takout Khouloud, Gargouri Faten, Tlili Karima, Rachdi Mohamed Amine, Ammar Hichem, Yedeas Dahmani, Radhouane Khaled, Chkili Ridha, Msakni Issam, Laabidi Besma. The Accuracy of pHH3 in Meningioma Grading: A Single Institution Study. Arch Pathol Clin Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.apcr.1001041; 8: 006-011
-
Assessment of Perceptions of Nursing Undergraduates towards Mental Health PracticesAlya Algamdii*. Assessment of Perceptions of Nursing Undergraduates towards Mental Health Practices. Clin J Nurs Care Pract. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjncp.1001059; 9: 007-011
-
Multipurpose Antioxidants based on Food Industry Waste: Production and Properties EvaluationToshkhodjaev*. Multipurpose Antioxidants based on Food Industry Waste: Production and Properties Evaluation. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001062; 9: 001-003
-
Relationship between Fertility Diet Score Index Items and Ovulation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Narrative ReviewHadis Alimoradi,Faezeh Mashhadi,Ava Hemmat,Mohsen Nematy,Maryam Khosravi,Maryam Emadzadeh,Nayere Khadem Ghaebi,Fatemeh Roudi*. Relationship between Fertility Diet Score Index Items and Ovulation in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Arch Food Nutr Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.afns.1001061; 8: 041-048
-
Evaluation of the LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for large-scale population testing in SenegalMoustapha Mbow*,Ibrahima Diallo,Mamadou Diouf,Marouba Cissé#,Moctar Gningue#,Aminata Mboup,Nafissatou Leye,Gora Lo,Yacine Amet Dia,Abdou Padane,Djibril Wade,Josephine Khady Badiane,Oumar Diop,Aminata Dia,Ambroise Ahouidi,Doudou George Massar Niang,Babacar Mbengue,Maguette Dème Sylla Niang,Papa Alassane Diaw,Tandakha Ndiaye Dieye,Badara Cisé,El Hadj Mamadou Mbaye,Alioune Dieye,Souleymane Mboup. Evaluation of the LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 antigen assay for large-scale population testing in Senegal. Int J Clin Virol. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001041; 6: 001-006
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available KnowledgeAvishek Mandal*. Prospective Coronavirus Liver Effects: Available Knowledge. Ann Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.acgh.1001039; 7: 001-010
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."